Q: What is high-oleic sunflower oil?

A. You pronounce it high "oh-lay-ick". High-oleic sunflower oil is a type of sunflower oil, bred to have a high concentration of the fatty acid oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid which is in rich supply in olive oil and macadamia nuts. It is also sold as Sunola or Monosun.
Regular sunflower oil is extracted from sunflower seeds and is naturally high in polyunsaturated fatty acids which belong to the omega-6 class such as linoleic acid. It has around 66 per cent polyunsaturates, although there's some variation depending on the variety and growing conditions. In detail, the breakup of the fat in regular sunflower oil is:
- Saturated 11%
- Monounsaturated 23%
- Polyunsaturated 66 %
- Total 100%
In contrast, to create an oil that's high in oleic acid, farmers have selected strains of sunflower that naturally have more monounsaturates (namely oleic acid) and less polyunsaturates (linoleic acid). These are not GM but the result of traditional plant breeding.
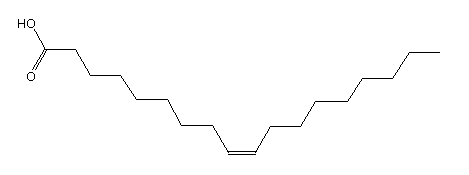
Here's a diagram of a molecule of oleic acid - note it has only one double bond of the monounsaturated fatty acid:
 Why?
Why?
Oils with less polyunsaturates are more stable during cooking and food manufacture. They are less likely to go rancid or to develop off-flavours and taints.
You'll spot high-oleic sunflower oil on packs of chips. It's used to deep-fry potato crisps and corn chips to give them a healthier fat profile. It's preferable to cooking in palm oil as it's low in saturated, has no trans fat and creates a good-tasting end result. Here's how sunflower oil compares to palm oil in percentages:
| Fat total and by type |
Palm oil |
High-oleic sunflower oil |
| Fat, total | 100 | 100 |
| Saturated | 50 | 10 |
| Monounsaturated | 49 | 85 |
| Polyunsaturated | 1 | 5 |
| Trans | Nil | Nil |
According to the US Sunflower Association, farmers now grow both types of sunflower oil. Here's a comparison of the saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats in regular sunflower oil with high-oleic sunflower oil:
|
Oil type |
Saturated
|
Monounsaturated |
Polyunsaturated
|
| Regular Polyunsaturated | 11% | 23% | 66% |
|
High-Oleic Monounsaturated |
9% | 82% |
9% |
Source: National Sunflower Association
There's research showing that substitution of saturated fat with foods rich in hi-oleic sunflower oil has favourable outcomes on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and factor VII activity. So this oil is another useful source of monounsaturated fats for diets aimed at prevention of heart disease.



